Fang Chen

Hi, this is Fang.
I define myself as a Genomics Data Scientist and currently work at Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center.
This is the Demo site for my projects and presentations.
My personal site is: To Fang's homepage
rareGWAMA is awesome!!
To The Liu Lab
The showcase for rareGWAMA
Project description: rareGWAMA is powerful and flexible to many tests. But meanwhile, it needs different information for a different test. So here we will give you some examples for the Conditional Single Variant Tests and the Gene Based Tests in real-life scenarios.
1. the Conditional Single Variant Tests
2. the Gene Based Tests
Suppose we have done some meta-analyses with multi-ancesity on the server.
2.1 pre-request
On the server, we will have following files:
- the score.stat.file:The statistics summary files, like:
less clean-CHS_CPD.MetaScore.assoc.gz
CHROM POS REF ALT N_INFORMATIVE AF INFORMATIVE_ALT_AC CALL_RATE HWE_PVALUE N_REF N_HET N_ALT U_STAT SQRT_V_STAT ALT_EFFSIZE PVALUE
1 10177 A AC 2352 0.5 2352 1 0 0 2352 0 1.67496 2.51553 0.264695 0.505508
1 10235 T TA 2352 0 0 1 1 2352 0 0 -0.108472 0.207841 -2.51104 0.601742
1 10352 T TA 2352 0.5 2352 1 0 0 2352 0 0.665562 2.61389 0.0974122 0.799013
1 10539 C A 2352 0 0 1 1 2352 0 0 -0.00020902 0.0626305 -0.0532862 0.997337
- imp.qual.file: The imputation quality file for each summary file, like:
less topmed.impqual.gz
CHROM POS REF ALT Rsq
1 13380 C G 1
1 16071 G A 1
1 16141 C T 1
1 16280 T C 1
1 49298 T C 1
1 54353 C A 1
1 54564 G T 1
1 54591 A G 1
then, we could make a list for all of them: the THREE columns are study name, the score.stat.file, and imp.qual.file, looks like:
less cpd.topmed-GSCAN1.index
AMISH ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freeze6a-Jan20-2019/clean/clean-AMISH_cpd.MetaScore.assoc.gz ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freezeDec20/clean/topmed.impqual.gz
ARIC ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freeze6a-Jan20-2019/clean/clean-ARIC_CPD.MetaScore.assoc.gz ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freezeDec20/clean/topmed.impqual.gz
BAGS ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freeze6a-Jan20-2019/clean/clean-BAGS_Asthma_CPD.MetaScore.assoc.gz ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freezeDec20/clean/topmed.impqual.gz
Boston ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freeze6a-Jan20-2019/clean/clean-Boston_CPD.MetaScore.assoc.gz ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freezeDec20/clean/topmed.impqual.gz
CHS ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freeze6a-Jan20-2019/clean/clean-CHS_CPD.MetaScore.assoc.gz ~/projects/GSCAN/TOPMed/freezeDec20/clean/topmed.impqual.gz
- vcf.ref.file: The reference panel file, e.g. could be downloaded from 1000 Genomes Project, as:
ls chr*.vcf.*
chr10.pass.vcf.gz
chr10.pass.vcf.gz.scIdx
chr18.pass.vcf.gz
chr4.pass.vcf.gz
chr11.pass.vcf.gz.scIdx
chr19.pass.vcf.gz
chr19.pass.vcf.gz.scIdx
...
Make sure the sample ids match the ref.ancestry we will see later.
zgrep -v "##" chr10.pass.vcf.gz|less
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT samp1 samp2 samp3 samp4 samp5 samp6 samp7
chr10 10438 . T G 120 PASS AVGDP=31.368;AC=1;AN=208576;AF=5e-06;SVM=-0.295252 GT 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0
chr10 10441 . C T 112 PASS AVGDP=31.5283;AC=1;AN=208802;AF=5e-06;SVM=-0.226377 GT 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0
chr10 10449 . T C 20 PASS AVGDP=31.8245;AC=1;AN=209260;AF=5e-06;SVM=-0.466546 GT 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0
chr10 10482 . AAT A 35 PASS AVGDP=28.4872;AC=1;AN=208606;AF=5e-06;SVM=0.10148 GT 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0
...
- anno: The annotation file
less cpd.var.tmp.txt.anno
chrom pos ref alt af anno gene
1 56582 T G 0.0261888 Intergenic Intergenic
1 62360 T C 0.00303632 Intergenic Intergenic
1 64931 G A 0.0907711 Intergenic Intergenic
1 77027 T G 0.0258075 Intergenic Intergenic
1 98618 TTGAC T 0.0320316 Intergenic Intergenic
1 105800 C T 0.00215033 Intergenic Intergenic
1 258023 C G 0.00267628 Intergenic Intergenic
- gene list: Could be any gene list you provide, or you could make the whole gene list based on the annotation file
grep -v "Intergenic" ai.var.tmp.txt.anno|cut -f7|sort|uniq > gene_list/gene.list
less gene_list/gene.list
LOC100133331
LOC100288069
FAM87B
LINC00115
LINC01128
FAM41C
LINC02593
SAMD11
NOC2L|SAMD11
NOC2L
KLHL17
...
if you want to test all the ~20k genes, it’s better to chop them into samll lists with 200 genes each. So you could run the tests parallelly later. You could use:
split gene_list/gene.list -l 200 my_gene
ls gene_list/my_gene*
gene_list/my_geneaa
gene_list/my_geneab
gene_list/my_geneac
gene_list/my_genead
...
- ref.ancestry: The ancestry information for each sample, as:
less ref.ancestry
fid ancestry study
samp1 HIM HCHS
samp2 HIM HCHS
samp3 HIM HCHS
samp4 HIM HCHS
samp5 HIM HCHS
...
- gc file: genomic control for each study:
less cpd.gc.txt
23andMe3 1.09 1.02
AACAC 1.02 0.98
ALSPAC 1.01 1
AMISH 1.027 1.397
ARIC 0.973 0.999
...
2.2 Running the test in R
Base on all the files in 2.1, we are ready to run the test in R
## load packages
library(rareGWAMA)
library(data.table)
## read all the files
index <- read.table("cpd.topmed-GSCAN1.index", as.is=TRUE);
score.stat.file <- index[, 2];
imp.qual.file <- index[, 3];
gc <- read.table("cpd.gc.txt", header=F, as.is=T);
ref.ancestry.tmp <- read.table('ref.ancestry', header=T, as.is=TRUE, sep='\t');
ref.ancestry <- cbind(ref.ancestry.tmp[,1], paste(ref.ancestry.tmp[,2], ref.ancestry.tmp[,3], sep=","))
study.ancestry.tmp <- read.table("cpd.study.assign.MDS.3.txt"), header=F, as.is=T);
ix.match <- match(index[,1], study.ancestry.tmp[,1]);
study.ancestry <- study.ancestry.tmp[ix.match, 2];
the ref.ancestry and study.ancestry objects should look like:
r$> head(ref.ancestry)
[,1] [,2]
[1,] "samp1" "HIM,HCHS"
[2,] "samp2" "HIM,HCHS"
[3,] "samp3" "HIM,HCHS"
[4,] "samp4" "HIM,HCHS"
[5,] "samp5" "HIM,HCHS"
...
r$> head(study.ancestry)
[1] "AACAC" NA "ARIC" "BAGS" "EUR" "CHS"
Please note, right now, rareGWAMA will throw error messages if the is NAs in study.ancestry file.
So, we should replace all the NAs with EURs for convinience.
study.ancestry[is.na(study.ancestry)] <- "EUR";
Finally, read the annotation file and gene list.
## read annotation file and choose the variation types you nedd
varFile <- as.data.frame(fread('ai.var.tmp.txt.anno', header=T));
## read the gene list
gene.vec <- read.table("./gene_list/my_geneaa", header=F);
gene.vec <- gene.vec[gene.vec!="Intergenic"];
anno <- varFile[which(varFile[,7]%in%gene.vec), 1:7];
r$> head(anno)
chrom pos ref alt af anno gene
20 1 727233 G A 0.01349950 Exon LOC100133331
21 1 727242 G A 0.16290000 Exon LOC100133331
29 1 766399 GAATA G 0.05111780 Deletion LOC100288069
30 1 769257 G A 0.08953040 Intron LOC100288069
31 1 769283 G A 0.00634359 Intron LOC100288069
32 1 770502 G A 0.07119060 Intron LOC100288069
...
2.2 Run the test
Now, since we have loaded all your files, we are ready to run the test:
## choose the method in R
rv_md <- "SKAT" ## or "VT", or "BURDEN"
res.gene <- rareGWAMA.gene(score.stat.file, imp.qual.file=imp.qual.file,
vcf.ref.file,refFileFormat="vcf.vbi",
anno=anno, annoType=c('Nonsynonymous', 'Stop_Gain', "Essential_Splice_site"),
rvtest=rv_md, ref.ancestry=ref.ancestry,
trans.ethnic=TRUE, study.ancestry=study.ancestry,
maf.cutoff=0.01);
res <- res.gene$res.formatted %>% as.data.frame
write_tsv(res, './results/cpd_SKAT_my_geneaa', na = "NA") ## here we use `write_tsv` from dplyr, or you could use `write.table`
2.3 Summarize the results
Now we have the result in the folder:
less cpd_SKAT_my_geneaa
GENE RANGE STAT P-VALUE MAF_CUTOFF NUM_VAR TOTAL_MAF POS_VAR N "NA"
LOC100133331 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
LOC100288069 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
SAMD11 1:930285-942951 2.89 0.15 0.000794070232285973 2 0.00134 1:930285_G/A,1:939121_C/T 29490 NA
NOC2L|SAMD11 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
NOC2L 1:946538-953858 NULL NULL 0 0 NA NA NA
KLHL17 1:962773-962773 1.05 0.305 0.000919175792572662 1 0.000919 1:962773_C/A 31963 NA
PLEKHN1 1:971135-974343 0.442 0.686 0.000317137298607967 2 0.00111 1:971135_C/T,1:974343_G/A 12330 NA
PERM1 1:976215-981169 NULL NULL 0 0 NA NA NA
And maybe we will have bunch of them if we run the tests parallelly.
ls cpd_SKAT_my_gene*
cpd_SKAT_my_geneaa
cpd_SKAT_my_geneab
cpd_SKAT_my_geneac
cpd_SKAT_my_genefd
...
You could gather them together
for f in cpd_SKAT_my_gene*; do tail -n +2 $f >> cpd_SKAT_all; done
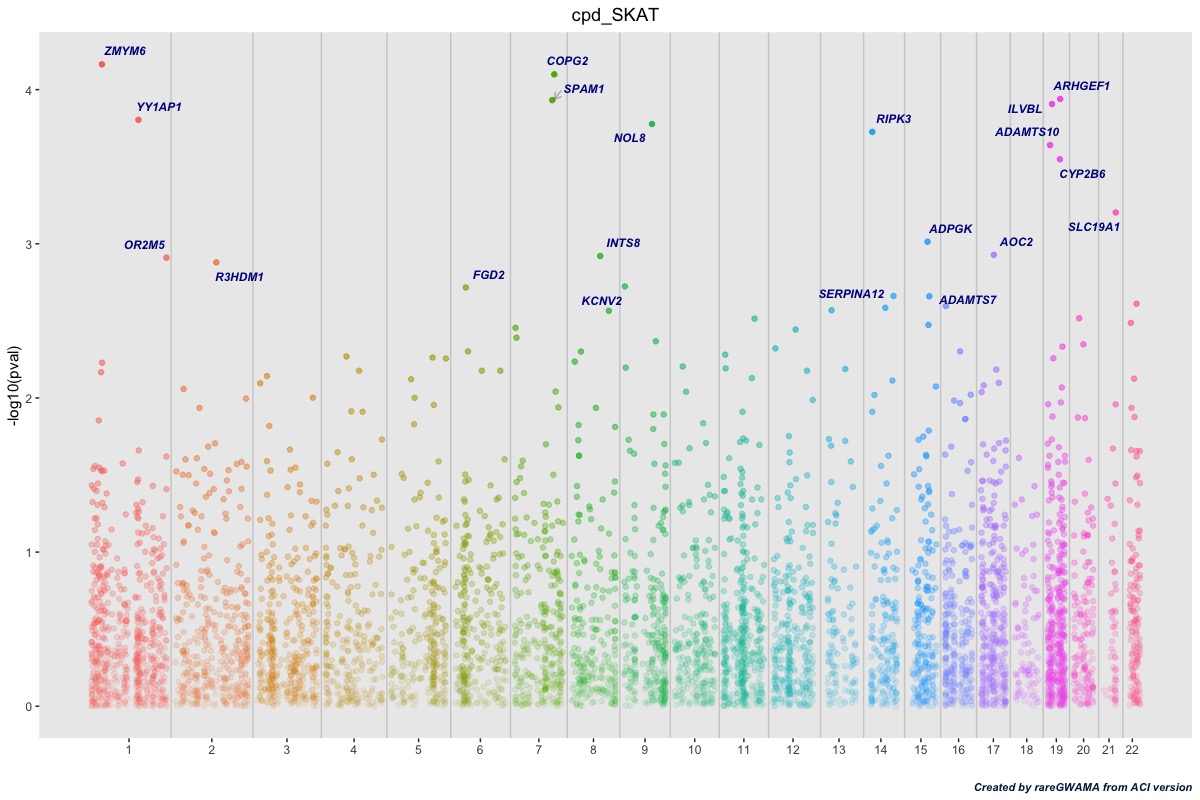
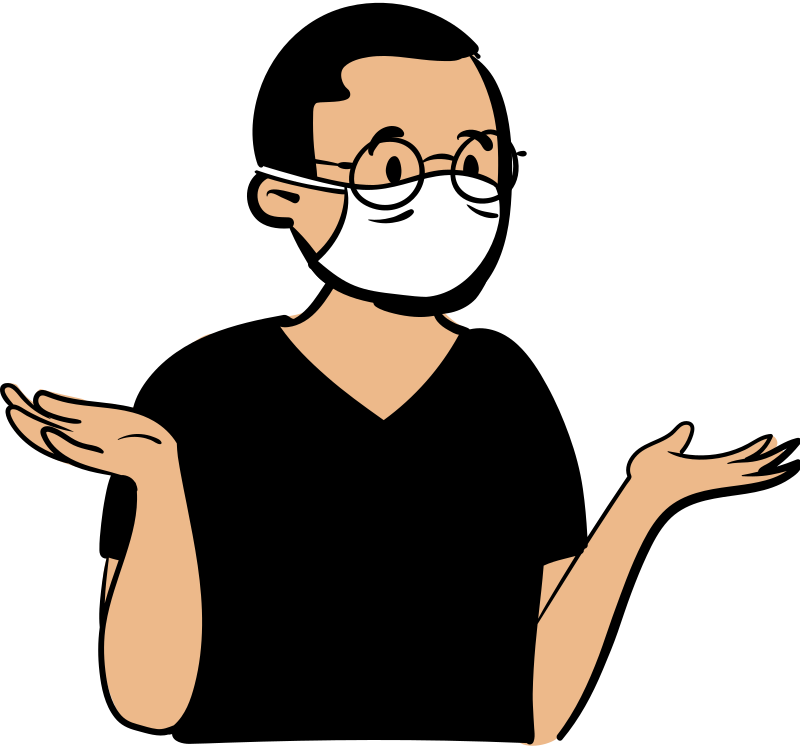
Use the R scprit here for the Manhattan plot:
r$>
gene_plot <- manhattan_for_genes("cpd_SKAT_all", top=20, main_title = "CPD at SKAT")
gene_plot
It should be like this: